
Instrument or a Steinmann pin used as a joystick in the femoral head. Pin, and the proximal fragment is lifted anteriorly with a blunt curved Theįracture is manually distracted by lateral and distal traction on the Lateral aspect of the proximal femur distal to the planned insertion of Technique to aid reduction is placement of a 5-mm Schanz pin in the 1 nonabsorbable suture for retraction.Ī head lamp is very helpful to provide illumination. Necessary, the capsule is dissected from the intertrochanteric ridge,Īnd its edges tagged with a no. The surgeon must be convinced that the fracture is anatomically reducedīefore using the limited open technique. Of fracture displacement or age of the patient ( 10). Osteoarthrosis and are therefore best treated with ORIF.Īn intracapsular hematoma under significant pressure isĮncountered in approximately 15% of patients regardless of the amount Means have been shown to be at greater risk for avascular necrosis and To this index, fractures that are not satisfactorily reduced by closed Should be within 20 degrees of the normal 180-degree value. Values more thanġ80 degrees and less than 160 degrees indicate unacceptable valgus and
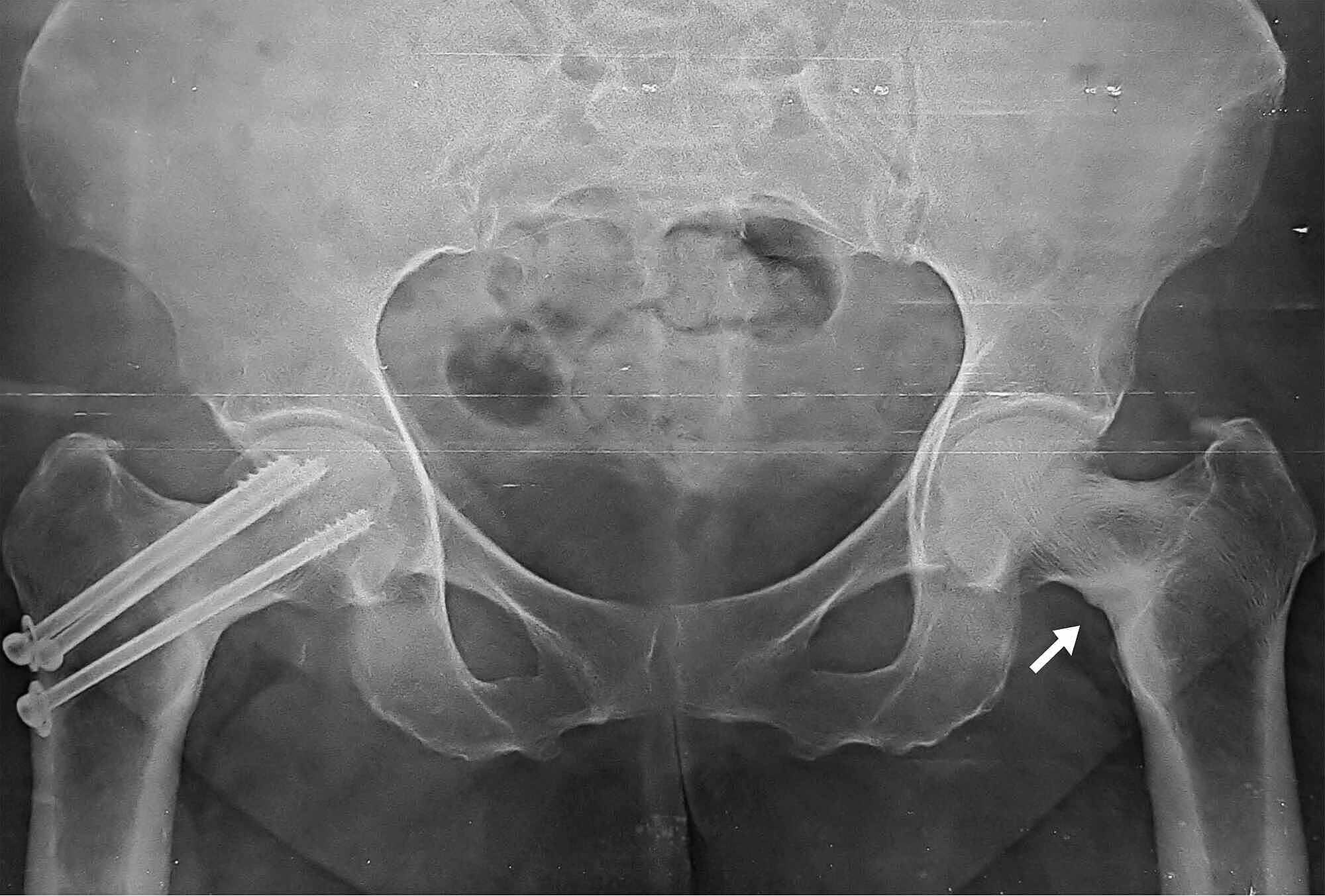
It should measure between 180 degrees and 160 degrees. The medial cortex of the proximal femoral shaft should be maintained. On the anteroposterior (AP) view, theĪngle between the central axis of the medial trabeculae of the head and Index for acceptable reduction is useful in determining the need for Patient of any age who has adequate bone density. Is not satisfactorily reduced using closed means. The primary indication for open reduction and internalįixation (ORIF) of a femoral neck fracture is a displaced fracture that


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
